Big data pipeline
A pipeline is a combination of processes that deal with some specific objects. Therefore, big data pipeline in computer science, can be interpreted as a workflow that capable to process huge amount of data.
A big data pipeline can be very complicate. Here is a big data pipeline that I used to work on:
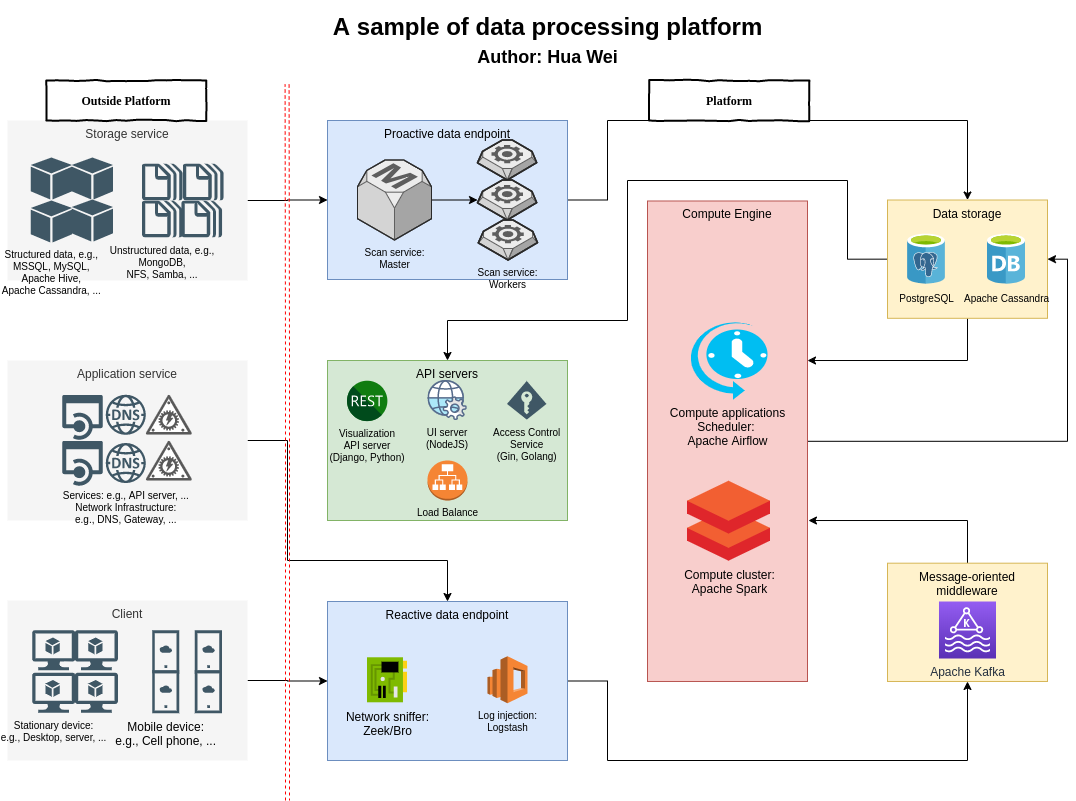
In this data processing platform, both dynamic network data and static data in data store are collected by data processing endpoint proactively or reactively. Then, collected data will be sent to persistence layer: either data storage or message-oriented middleware. After that, compute cluster, which is managed by DAG scheduler, will try to process data in batch mode. Finally, the result of compute engine will be demonstrated with API server and user interface. Every component is carefully designed and programmed to support both functionality and scalability requirements. In this article, I focused on the compute engine part, which is using Apache Spark as compute cluster and Apache Airflow as scheduler. The design of the compute engine is shown in the figure below:
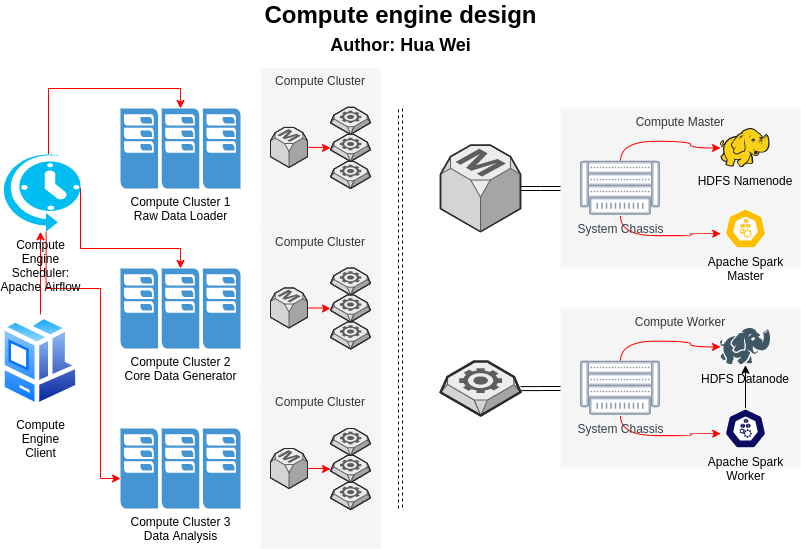
As we can see, compute cluster contains two types of node: compute master and compute worker. Both compute master and compute work have a system chassis, which responsible for the control path of the whole platform. The compute master has Apache HDFS namenode and Apache Spark master, while compute work has Apache HDFS datanode and Apache Spark worker. There are three compute clusters in the compute engine. Different compute cluster takes different types of computational application. The computational applications are scheduled by the Apache Airflow. Notice that this is a very naive design to achieve basic functionality. Multiple improvements, like redundant compute master for high availability, lambda architecture to cover stream mode, etc., are not covered in this article.
Apache Spark
Why Apache Spark
Apache Spark is an open source distributed compute engine that support both batch and stream processing. Apache Spark is well-know for its DAG optimization over map reduce tasks, which reduce the disk IO, and keep data in memory for computation as much as possible. Apache Spark is a good replacement on Apache Hadoop in batch processing area. In stream processing field, Apache Spark also does a good job to use micro-batch to simulate streaming data. However, there are other candidates, like Apache Storm, Apache Flink, using real stream processing, and out perform Apache Spark in some streaming data scenario. But, in general, Apache Spark is a good distributed computation framework that cover both batch and stream processing.
Apache Spark Applications
As described in the platform requirement above, it would be reasonable to have four applications to achieve system design targets:
- StaticDataProcessor: Processing static data, which comes from datastore scan service.
- DynamicDataProcessor: Processing dynamic data, which comes from network sniffer or log injection.
- CoreDataGenerator: Combine the static and dynamic data together to generate core features (e.g., entity resolution).
- AnalyticDataGenerator: Analyze on core features and derive analytic result for API server.
To keep system as simple as possible, the batch mode processing is enough to satisfy requirements. To achieve “Exactly one time” processing, checkpoint system, which is a record on data start and end timestamps, is added on all applications. An demo code of these applications can be found at this github link.
Apache Airflow
As you may already noticed, there are dependencies between applications, and a full cycle of operation can be viewed as a directed acyclic graph (DAG):
Of course, one can use a bash script to execute applications sequentially, or python script to execute in a topological order of DAG. However, there are already mature open source projects that have not only DAG workflow, but also visualization, persistance interface and distributed maintaince. Apache Airflow is one of the best of these projects, and it is choosen to be the compuataion applications scheduler.
Here is one example to build Apache Airflow DAG with python script: compute_engine_application_scheduler.py.
- One can first initialize Apache Airflow database by:
airflow initdb
- Then, start webserver with command:
airflow webserver --port 8080
- Add DAG and test it:
python3 compute_engine_application_scheduler.py
airflow test compute_engine_application_scheduler 2020-05-01
- Check your DAG with this url:
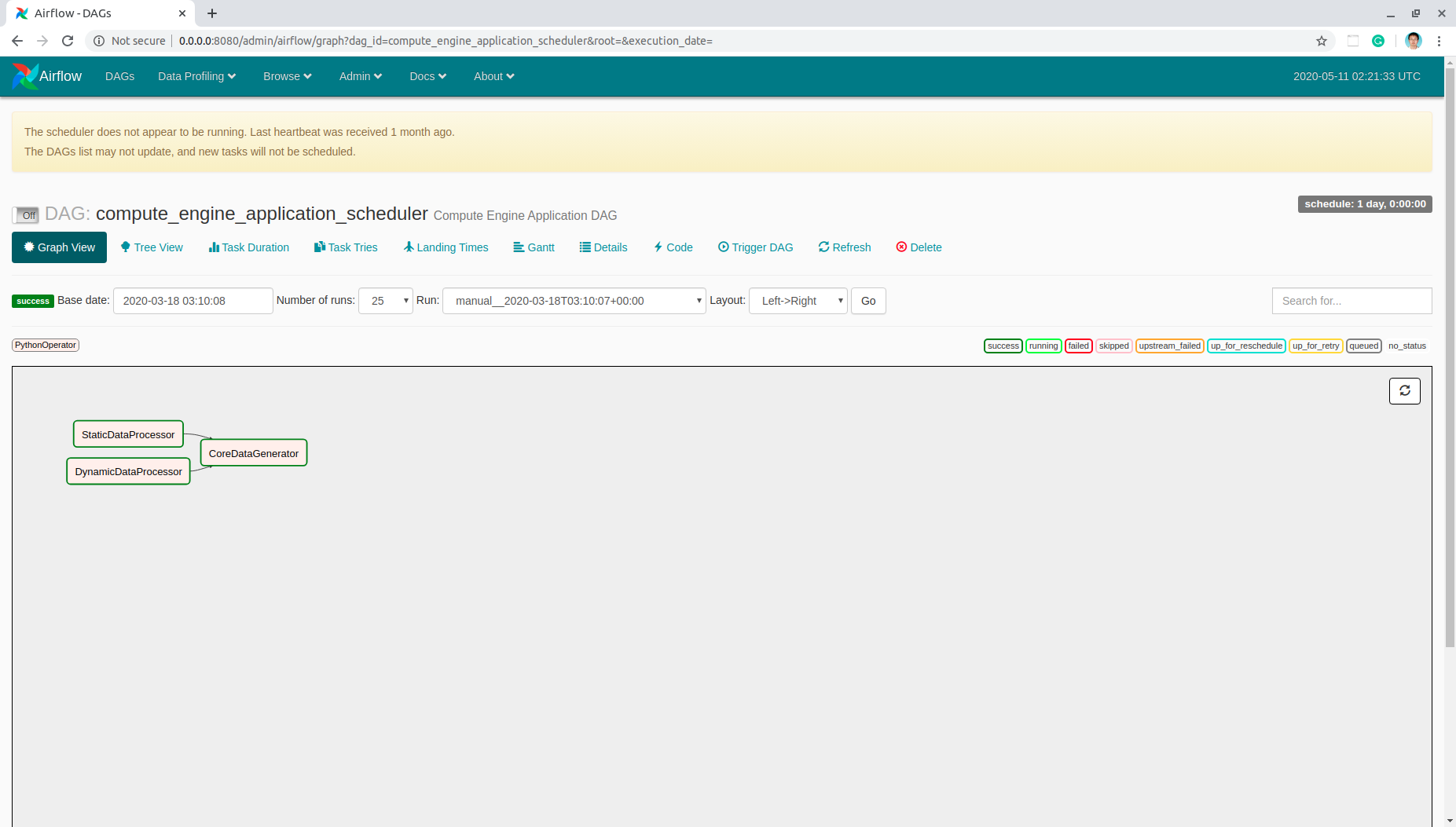
- Enable the newly added DAG:
airflow scheduler